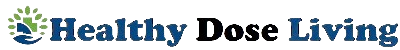Not taking vitamin B12 supplements or regularly eating B12-fortified foods may explain the higher stroke risk found among vegetarians.
Leonardo da Vinci had a stroke. Might his vegetarian diet have been to blame? “His stroke…may have been related to an increase in homocysteine level because of the long duration of his vegetarian diet.” A suboptimal intake of vitamin B12 is common in those eating plant-based diets (unless they take B12 supplements or regularly eat B12-fortified foods) and can lead to an increased level of homocysteine in the blood, which “is accepted as an important risk factor for stroke.”
“Accepted” may be overstating it as there is still “a great controversy” surrounding the connection between homocysteine and stroke risk. But, as you can see in the graph below and at 0:57 in my video Vegetarians and Stroke Risk Factors: Vitamin B12 and Homocysteine?, those with higher homocysteine levels do seem to have more atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries that lead up to the brain, compared to those with single-digit homocysteine levels, and they also seem to be at higher risk for clotting ischemic strokes in observational studies and, more recently, bleeding hemorrhagic strokes, as well as increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease and all causes put together.
Even more convincing are the genetic data. About 10 percent of the population has a gene that increases homocysteine levels by about 2 points, and they appear to have significantly higher odds of having a stroke. Most convincing would be randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials to prove that lowering homocysteine with B vitamins can lower strokes, and, indeed, that appears to be the case for clotting strokes: Strokes with homocysteine-lowering interventions were more than five times as likely to reduce stroke compared with placebo.
Ironically, one of the arguments against the role of homocysteine in strokes is that, “assuming that vegetarians have lower vitamin B12 concentrations than meat-eaters and that low vitamin B12 concentrations cause ischaemic stroke, then the incidence of stroke should be increased among vegetarians…but this is not the case.” However, it has never been studied until now.
As you can see in the graph below and at 2:16 in my video, the EPIC-Oxford study researchers found that vegetarians do appear to be at higher risk.
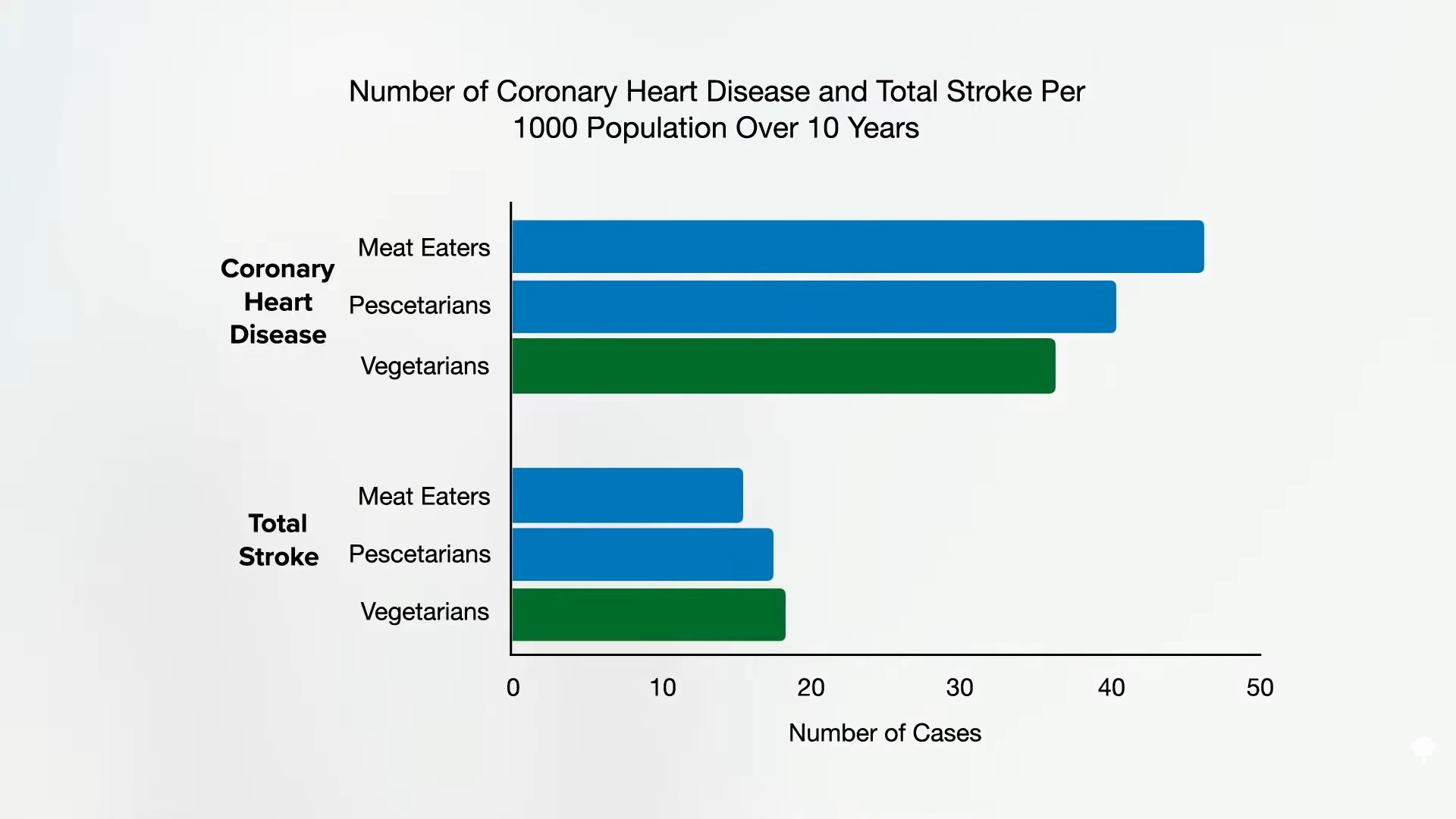
And no wonder, as about a quarter of the vegetarians and nearly three-quarters of the vegans studied were vitamin B12-depleted or B12-deficient, as you can see below and at 2:23, and that resulted in extraordinarily high homocysteine levels.
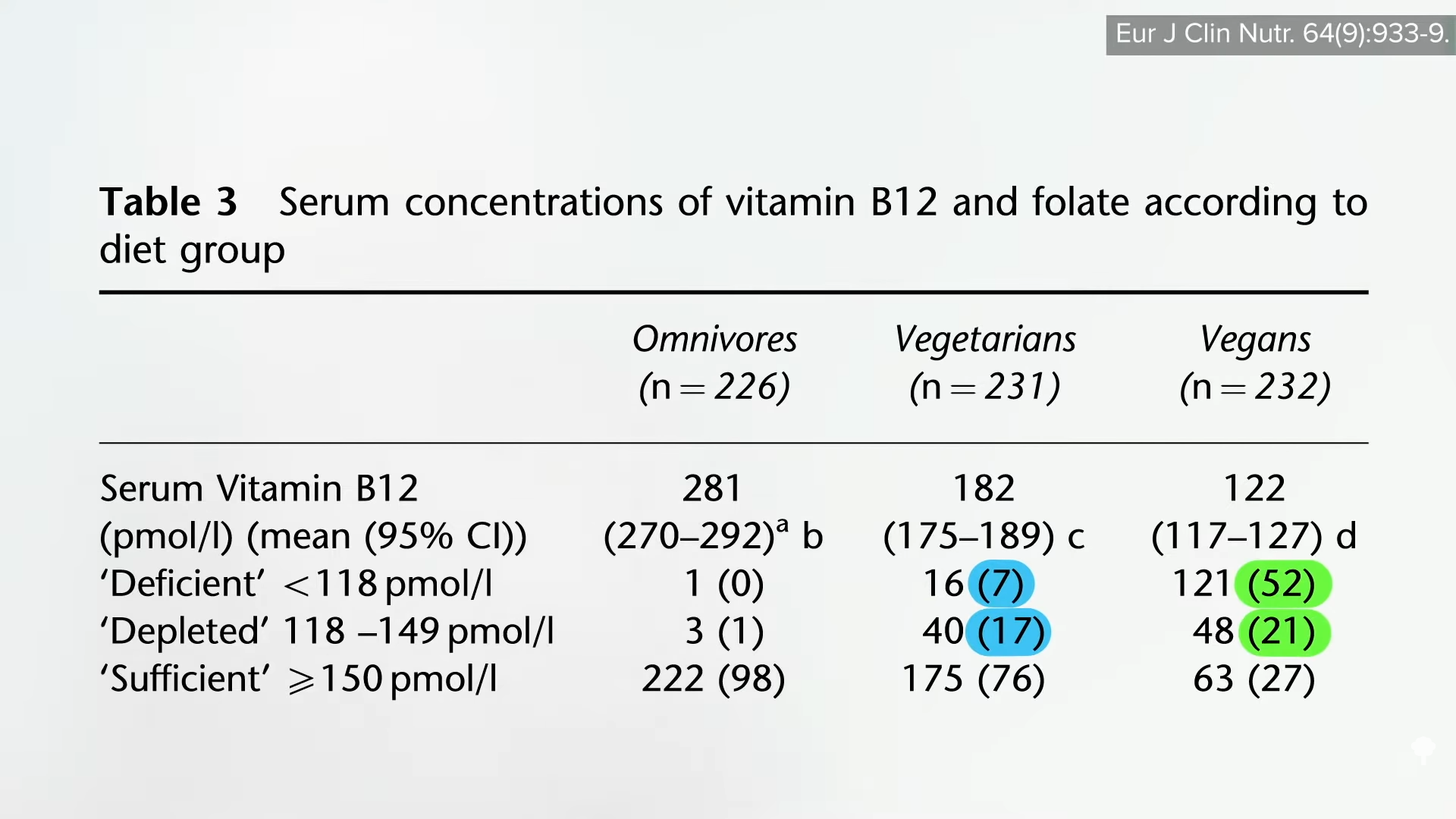
Why was there so much B12 deficiency? Because only a small minority were taking a dedicated B12 supplement. And, unlike in the United States, B12 fortification of organic foods isn’t allowed in the United Kingdom. So, while U.S. soymilk and other products may be fortified with B12, UK products may not. We don’t see the same problem among U.S. vegans in the Adventist study, presumably because of the B12 fortification of commonly eaten foods in the United States. It may be no coincidence that the only study I was able to find that showed a significantly lower stroke mortality risk among vegetarians was an Adventist study.
Start eating strictly plant-based without B12-fortified foods or supplements, and B12 deficiency can develop. However, that was only for those not eating sufficient foods fortified with B12. Those eating plant-based who weren’t careful about getting a regular reliable source of B12 had lower B12 levels and, consequently, higher homocysteine levels, as you can see below and at 3:27 in my video.
The only way to prove vitamin B12 deficiency is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease in vegetarians is to put it to the test. When researchers measured the amount of atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries, the main arteries supplying the brain, “no significant difference” was found between vegetarians and nonvegetarians. They both looked just as bad even though vegetarians tend to have better risk factors, such as lower cholesterol and blood pressure. The researchers suggest that B12 deficiency plays a role, but how do they know? Some measures of artery function weren’t any better either. Again, they surmised that vitamin B12 deficiency was overwhelming the natural plant-based benefits. “The beneficial effects of vegetarian diets on lipids and blood glucose [cholesterol and blood sugars] need to be advocated, and efforts to correct vitamin B12 deficiency in vegetarian diets can never be overestimated.”
Sometimes vegetarians did even worse. Worse artery wall thickness and worse artery wall function, “raising concern, for the first time, about the vascular health of vegetarians”—more than a decade before the new stroke study. Yes, their B12 was low, and, yes, their homocysteine was high, “suggest[ing] that vitamin B12 deficiency in vegetarians might have adverse effects on their vascular health.” What we need, though, is an interventional study, where participants are given B12 to see if that fixes it, and here we go. The title of this double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized crossover study gives it away: “Vitamin B-12 Supplementation Improves Arterial Function in Vegetarians with Subnormal Vitamin B-12 Status.” So, compromised vitamin B12 status among those eating more plant-based diets due to not taking B12 supplements or regularly eating vitamin B12-fortified foods may explain the higher stroke risk found among vegetarians.
Unfortunately, many vegetarians resist taking vitamin B12 supplements due to “misconceptions,” like “hold[ing] on to the old myth that deficiency of this vitamin is rare and occurs only in a small proportion of vegans.” “A common mistake is to think that the presence of dairy products and eggs in the diet, as in LOV [a lacto-ovo vegetarian diet], can still ensure a proper intake [of B12]…despite excluding animal flesh.”
Now that we may have nailed the cause, maybe “future studies with vegetarians should focus on identifying ways to convince vegetarians to take vitamin B12 supplements to prevent a deficiency routinely.”
I have updated my recommendation for B12 supplementation. I now suggest at least 2,000 mcg (µg) of cyanocobalamin once weekly, ideally as a chewable, sublingual, or liquid supplement taken on an empty stomach, or at least 50 mcg daily of supplemental cyanocobalamin. (You needn’t worry about taking too much.) You can also have servings of B12-fortified foods three times a day (at each meal), each containing at least 190% of the Daily Value listed on the nutrition facts label. (Based on the new labeling mandate that started on January 1, 2020, the target is 4.5 mcg three times a day.) Please note, though, that those older than the age of 65 have only one option: to take 1,000 micrograms a day.
We started this series on what to eat and not eat for stroke prevention, and whether vegetarians really have a higher stroke risk. Check related posts for the last few videos that looked at specific factors.
Stay tuned for: